Central air conditioner compressors
It made the refrigerant flows!
What are air conditioner compressors?
Air conditioning compressor is the heart of the AC units. It’s the mechanical components that use electricity and capacitor as the single energy source to operate it.
The air conditioning compressor is the ac parts that cause the refrigerant to flows in a cycle.

This compressor is not for residential, it is for commercial.
What are the types of air conditioning compressors?
There are five main types of air conditioner compressors:
- Reciprocating
-
Rotary compressor
- Centrifugal compressor
- screw compressors
- Scroll compressors
All five groups of HVAC compressors work the same way, but their internal methods of compressing refrigerant vapors are different.
The most common compressor is the reciprocating compressor. It comes into two domes or housing:
- Open compressors
- Hermetic compressors
Hermetic compressor is the most common air conditioner compressors found in residential AC units and light commercial units. So, the only compressor we’ll being focusing here is hermetic compressors.

Hermetic compressor comes into two types:
- Sealed or welded hermetic compressors
- Semi-hermetic (this compressor has nuts and bolts holding it together.)
Sealed hermetic compressors
Welded hermetic compressors aka tin can or sealed hermetic are throwaway compressors. There is no way of get inside the compressor, unless it’s cut open.
There’re few companies that open this compressor, they are specialize in this kind of works. The compressors manufacture opens the sealed hermetic compressors to examine it. Otherwise, it’s a throwaway.
In sealed hermetic compressors the motor and crankshaft are in vertical position. It used the suction refrigerant from the air conditioner evaporator to cool the internal compressor at an operating temperature.
The air conditioner compressors have a safety device inside to protect the compressor from heating.
This device is internal overload. The air conditioning compressor is the most expensive AC parts in condenser units; it’s wise to protect the compressor.
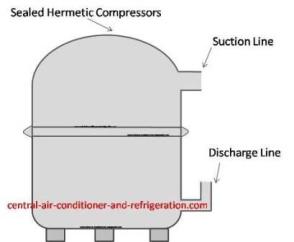
In a hermetic compressor there’re two important tubes that welded with the hermetic shell. These two tubes are:
- Suction line
- Discharge line

The suction line is the larger line connecting to the indoor air conditioner evaporator. The AC compressors pull the refrigerant through the suction line and releases it to the air conditioner condenser through the discharge line.
In split-central air conditioner units, the suction is always insulating to prevent the cool refrigerant from absorbing outside heat.
Semi-hermetic compressors
This is the air conditioning compressors that have nuts and bolts. The motor and the compressor are inside the heavy iron cast. This is the compressor that can be fixed by removing the bolts and shells that holding it together.
This is commercial HVAC compressor, in residential, it’s smaller.

There aren’t many residential that used these types of compressor, but we could find it in larger home and light commercial. It can be fixed in the field, if we have the necessary air conditioner equipment.
How does a central air conditioner compressor works?
The HVAC compressors works by using an electricity to energize the motor; which it turns cause compressor crankshaft to rotates.
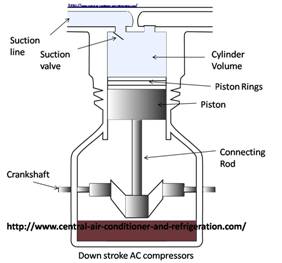
Reciprocating compressors are a piston-cylinder type of pump. The main parts include a cylinder, piston, connecting rod, crankshaft, cylinder head and valves. The operating cycle of a reciprocating compressor is shown below.
On the down stroke of the piston, a low pressure area is created between the top of the piston, the cylinder head and the suction line of the air conditioning evaporator. Cold refrigerant vapor rushes through the suction valve inlet and into the low pressure area.
On the up stroke, the suction valve closes and the exhaust (discharge) valve is forced open with the increasing pressure. The vapor is compressed and forced into the discharge (high) side of the refrigeration system.
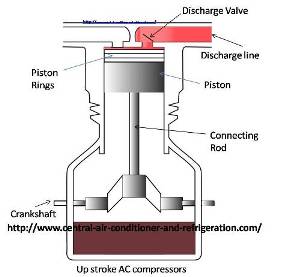
When the piston reaches the top of the cylinder, the discharge valve closes, and the suction valve opens as the piston starts down again drawing in cold refrigerant vapor to complete the cycle.
Note that the connecting rod attached between the crankshaft and piston serves to change rotary motion into reciprocating (back and forth) motion.
The piston rings prevent the vapor from escaping between the piston and cylinder walls and improve the operating efficiency.
The compressor housing or crankcase contains the bearing surfaces for the crankshaft and stores the oil that lubricates the compressor parts.
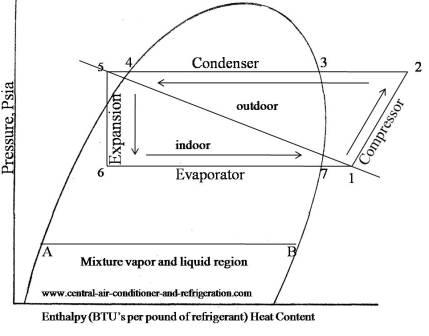
The process of the air conditioning compressors are showed between points 1 and 2 on the PH chart.
In split- central air conditioner, the compressor is located outside within the condenser units. It’s a vapor pump!
Compressors produce a pressure different between the low side (suction pressure) and high sides (discharge pressure) of the refrigeration system.
This is achieved by pulling of low pressure, low temperature, superheated refrigerant vapor from the suction (evaporator) side.
It pulls the correct amount of refrigerant to fill the volume. The refrigerant goes through the compressor, after it crosses the compressor it then creates a high temperature, high pressure superheated refrigerant vapor to the high pressure side (air conditioner condenser side).
The compression of the vapor causes the transfer of heat energy to flows from the low side to the high side of the system.
As the air conditioning compressors compression the refrigerant, additional heat is added to the refrigerant. These heats are:
- Heat of compression
- Mechanical friction heat
- Compressors winding heat
- Other suction line heat
The pressure different created by the operation of the compressor is responsible for refrigerant flow through the refrigeration cycle.
Read other central air conditioner parts
Air Conditioner expansion valve
Return to central air conditioner and refrigeration